How Is Water Purified in a Water Treatment Plant?
How Is Water Purified in a Water Treatment Plant?
How Is Water Purified in a Water Treatment Plant?
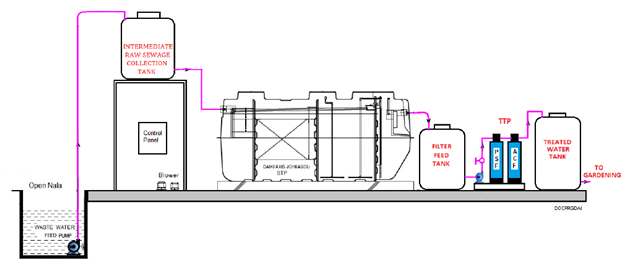
Water purification is a multi-stage process that removes contaminants and other impurities from water to make it safe for human consumption. The exact process used in a water treatment plant can vary depending on the quality of the source water and the level of treatment required, but typically involves the following steps:

Coagulation and Flocculation: Chemicals such as alum are added to the water to make suspended particles (e.g., dirt, bacteria) stick together and form larger clumps called flocs, which can be more easily removed.
Sedimentation: The water is allowed to sit in a tank, allowing the flocs to settle to the bottom. This process is known as sedimentation.
Filtration: The water is passed through multiple filters, such as sand or activated carbon, which remove any remaining particles and impurities.
Disinfection: The water is treated with a disinfectant such as chlorine or ultraviolet light to kill any remaining bacteria, viruses, or other pathogens that could cause disease.
pH Adjustment: Water is also tested for pH levels to ensure that it falls within the acceptable range.
Storage and distribution: After treatment, the purified water is stored in a reservoir or tank and distributed through a network of pipes to homes and businesses.
Overall, water treatment plants use a combination of physical, chemical, and biological processes to remove impurities and make water safe for human consumption.
How Is Water Purified in a Water Treatment Plant? Read More »